Cervical osteochondrosis has today become one of the most common diseases of the musculoskeletal system, which unfortunately affects not only the elderly but also the very young. Lack of physical activity, constant work on a computer, and other features of modern urban life negatively affect its condition and lead to the development of osteochondrosis.
In this article, we examine why it occurs, how it manifests itself, how it is treated, and which drugs are effective in treating cervical osteochondrosis, and we learn what non-drug methods exist.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is a degenerative-dystrophic characteristic change that disrupts the functional activity and structure of the spine. As a result, changes occur not only in the intervertebral plates themselves, but also in the vertebrae and cervical spine joints.
Causes of occurrence
With this disease, a devastating change occurs in the shock-absorbing ability of the vertebral discs, along with displacement. One reason for this change is the deposition of salts due to an increase in their levels in human blood and lymph fluid.
The main reason for the appearance of cervical osteochondrosis is the sedentary lifestyle. Office workers are most susceptible to this disease, spending most of their working time on paper and computer. In the absence of the necessary physical activity in the human body, blood flow slows down, and muscle tissue does not need the inflow of salts from food. As a result, salts are deposited in the cartilage tissue of the spine.
It contributes to the development of diseases and malnutrition, overweight and metabolic disorders, as well as persistent stress, nervous tension, sleep disorders.
In addition, the disease can occur due to trauma, extreme stress, inflammatory and other diseases.
Degrees of development
Depending on the severity of the symptoms and the extent of the functional impairment, we distinguish three stages:
First degree
It is characterized by minimal severity of symptoms. Patients usually notice general deterioration in well-being, headache, weakness, and dizziness. At this stage, there is a slight deformation and displacement of the cervical vertebrae, cracks appear in the tissue of the disc.
Second degree
The second stage of the disease is characterized by a significant increase in pain due to strong displacement of the intervertebral discs and pinching of the nerve roots.
Third degree
It is characterized by complete destruction of the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc, which can lead to the formation of a hernia. The symptoms of the disease are pronounced at this stage. The patient feels severe weakness, headache, nausea, dizziness, sharp pain in his neck, radiates to the shoulder blades and shoulders. In some cases, the intensity of the symptoms associated with the replacement of the damaged area with connective tissue is temporarily reduced.
Fourth degree
With the complete destruction of the intervertebral disc, the destroyed disc replaces its connective tissue. Dizziness, increased tinnitus, impaired coordination are due to the fact that the artery that feeds the cerebellum and cervical lobe of the brain is involved in the process.
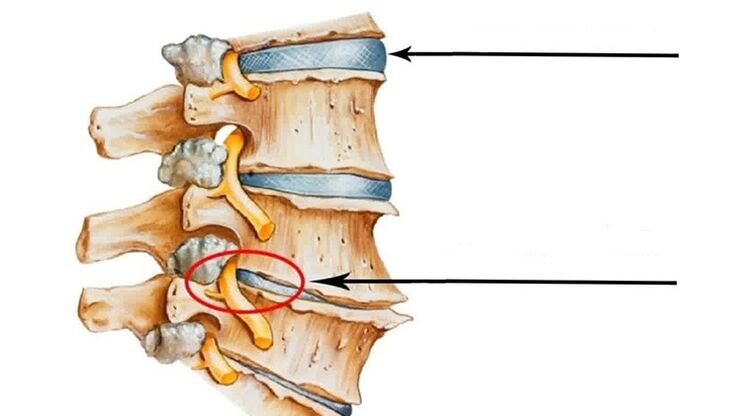
It is very important to diagnose the disease at an early stage and consult a specialist so that you know what you need to do to prevent further development.
Symptoms and signs
In addition to pain syndrome, osteochondrosis of the cervix can be accompanied by a variety of symptoms after feeling that a person may not be able to figure out the developing disease immediately. This is due to the fact that cervical spine dysfunctions inevitably affect the work of the cerebrovascular system.
There are three main groups of symptoms:
Pain syndrome
Neurological manifestations in the form of pain syndromes occurring at different sites. First, they are headaches of varying intensity and duration that can be given to the eye or ear. In this case, the pain usually does not go away after taking the painkillers. Aching or sharp pain in the neck and back of the head that radiates to the shoulder blades, forearms and elbows. With this disease, there is usually a dull, aching pain that then becomes more pronounced and spreads to different parts of the body.
Decreased sensitivity
Movement disorders that occur as a result of disruption of the normal functioning of the spinal cord. Patients may experience numbness and decreased tenderness in the extremities, deterioration in foot tone, weakness in the arms and legs, and goosebumps. Pain can occur when you raise your arm or move it to the side.
Weakness
Signs of vascular disorders of the brain, which have many manifestations. People with cervical osteochondrosis often feel severe weakness for no apparent reason and get tired quickly.
Noise in the ear
Often there is stuffy and noise in the ears, hearing loss and a sharp deterioration in well-being.
Mental disorders such as depression, anxiety syndrome, panic attacks are also possible.
Diagnostics
Basic diagnostic methods:
- X-ray.It is a poorly informative method, especially in the later stages of the disease.
- Computed tomography (CT).It shows vertebral abnormalities more effectively, but it is difficult to determine the size, the presence of a hernia, and the presence of a herniated spinal hernia (disco-medulla conflict).
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).The method that shows most of the information, clearly visible bone structures, intervertebral discs, hernias and their size, and the direction of their growth.
- Ultrasonic duplex scanning.This method is used when there is a suspicion of impaired blood flow in the arteries of the spine. This indicates a decrease in blood flow rate and obstruction of normal blood flow.
Treatment
The development of a treatment plan for cervical osteochondrosis depends primarily on the causes of the disease, the nature and intensity of its symptoms. As practice has shown, complex therapy has the greatest effect, which may include medication, massage, therapeutic practices, and a few other methods.
The treatment should be performed under the supervision of qualified specialists: vertebral neurologist, masseur, chiropractor, surgeon, neurologist. It is very important to see a doctor in time to prevent the development of the second and third stages of the disease. In this case, the treatment takes much longer until complete recovery.
Therapy is prescribed in a certain order:
- above all, pain relief is needed;
- then get rid of edema;
- prescribe drugs that restore blood circulation;
- muscle tissue is strengthened;
- measures are taken to repair damaged tissues.
Important!Keep in mind that exercise therapy is contraindicated during periods of disease exacerbation as it can cause complications.
As a first aid to alleviate acute pain syndrome during exacerbation, patients are prescribed analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the presence of acute pain. Warming and analgesic ointments and pepper stains are used instead of localizing muscle cramps. The swelling is well removed by diuretics. If the patient is numb in the limbs, special exercises should be performed to stimulate blood circulation.
It should be recalled that these measures relieve pain but do not eliminate the causes of the disease. Medications prescribed by your doctor in conjunction with other therapies will cope with this task.
Medicine
The goal of pharmacological treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is to relieve muscle pain and inflammation, restore blood circulation and strengthen the vascular system of the brain, and the general healing effect of the body.
Patients should be prescribed vitamin B supplements, which can be prescribed as tablets or intramuscular injections.
Chondroprotective drugs are prescribed to repair damaged cartilage tissue in intervertebral discs. Taking these medications should not be ignored as they will help strengthen bone tissue and prevent the disease from returning in the future.
Physiotherapy
During the performance of health-enhancing gymnastics, circular movements of the head must be performed, the neck leans left - right, forward - backward. Shoulder and arm movements should also be included in the series of exercises. Each movement should be performed smoothly, without rudeness and stress, alternating between the active phase and a little rest.
Conclusion
It is always easier to prevent disease than to cure it. To prevent the disease from developing, you need to follow a few simple rules:
- avoid extreme stress on the spine to avoid damage to the intervertebral discs;
- perform daily gymnastics on the whole body, focusing on the back muscles and especially the cervical spine;
- avoid nervous overload and fatigue, remember the importance of proper rest and proper sleep for the body;
- lead an active, active lifestyle, exercise more, walk in the fresh air, eat normally and in a balanced way, and give up bad habits as well.

















































